In today’s data-driven business landscape, understanding your customers isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Yet according to Harvard Business Review, only 15% of executives have a unified view of customer data, making it nearly impossible to craft effective digital experiences. This disconnect between data collection and actionable insights is where Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems come into play.
But here’s the challenge: CDP vs CRM isn’t actually a choice between one or the other. These two powerful platforms serve distinct yet complementary purposes in your customer data strategy. Understanding their differences, strengths, and how they work together can transform how you engage with customers and drive business growth.
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about CDPs and CRMs in 2025, from core differences and use cases to implementation strategies and real-world results. Whether you’re a marketing leader evaluating platforms, a sales director seeking better customer insights, or an executive planning your data strategy, this guide will help you make informed decisions.
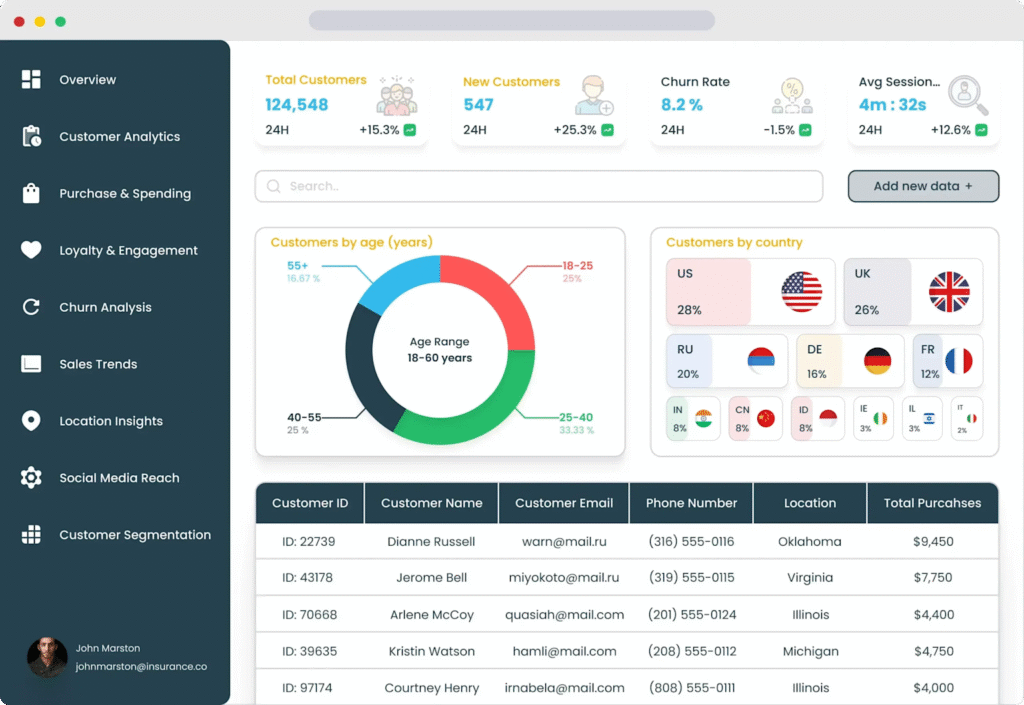
Customer insights dashboard displaying key customer metrics, demographics by age and country, and detailed customer data table (DronaHQ)
Understanding the Fundamentals
What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is specialized software that collects, cleanses, unifies, and organizes customer data from multiple sources into a centralized database. Unlike other data management systems, a CDP automatically integrates online and offline data—from website clicks and mobile app interactions to in-store purchases and customer service calls—creating comprehensive, real-time customer profiles.
Core CDP Capabilities:
- ✅ Automated Data Collection: Captures data via APIs, SDKs, code snippets, and pre-built integrations
- ✅ Identity Resolution: Unifies data from disparate sources into single customer profiles
- ✅ Real-Time Processing: Updates customer profiles instantly as new data arrives
- ✅ Audience Segmentation: Creates dynamic segments based on behaviors and attributes
- ✅ Data Activation: Sends unified data to marketing, analytics, and operational tools
- ✅ Privacy Compliance: Manages consent, data masking, and regulatory requirements (GDPR, CCPA)
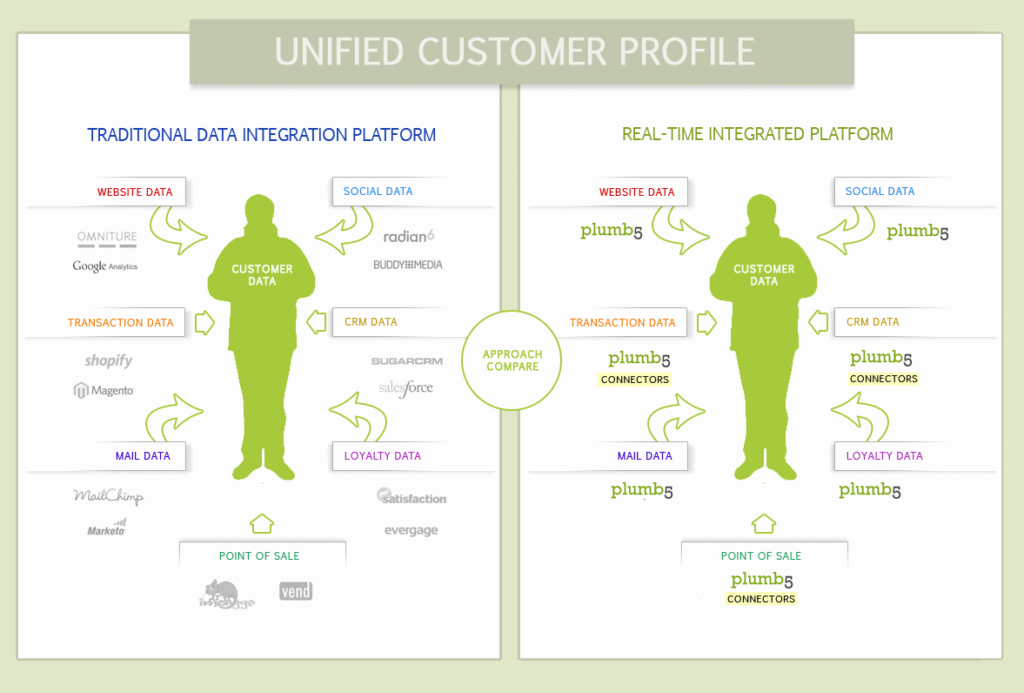
Comparison of traditional data integration platforms and real-time integrated platforms for unifying customer profiles (blackbox4.wordpress.com)
Who Uses CDPs?
While designed for cross-functional use, CDPs primarily benefit:
- Marketing Teams: For personalization, campaign targeting, and customer journey orchestration
- Product Teams: To understand feature usage and optimize user experiences
- Analytics Teams: For advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and business intelligence
- Leadership: To gain holistic view of customer behavior and strategic insights
What is a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System?
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is software designed to manage and improve interactions with existing and potential customers, particularly in sales and customer support contexts. CRMs centralize contact information, communication history, and transaction details, helping teams build and nurture customer relationships.
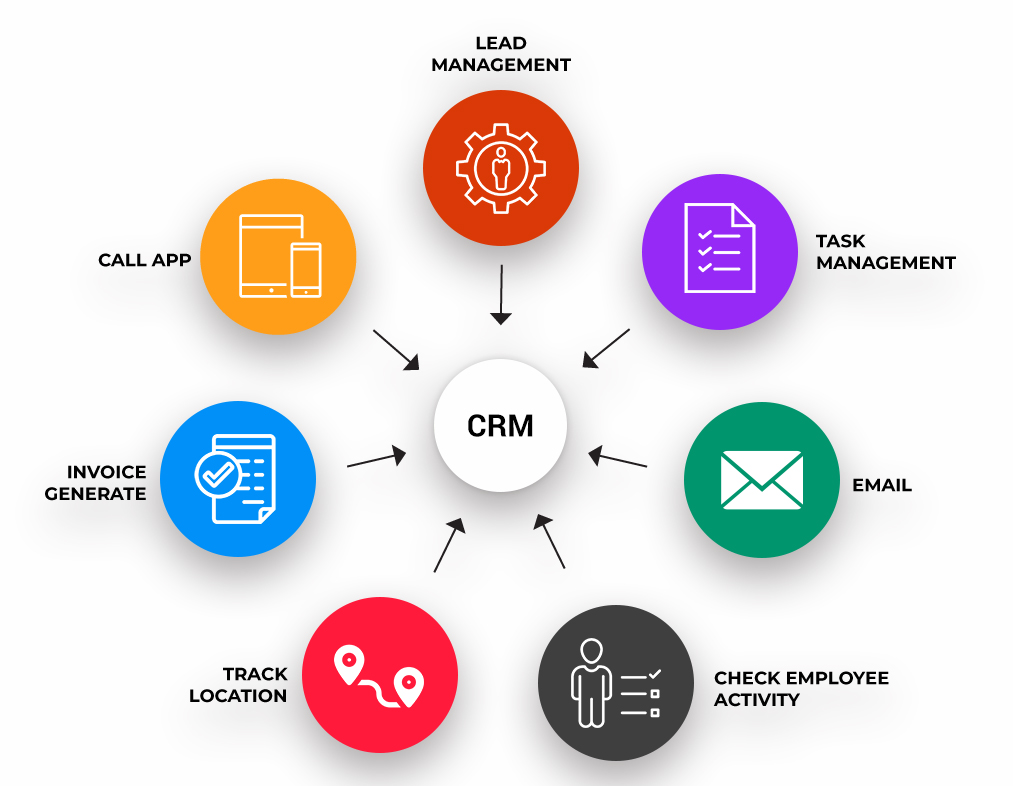
Key functions of a CRM system include lead management, task management, email, employee activity tracking, location tracking, invoice generation, and call application (Ntrixit)
Core CRM Capabilities:
- ✅ Contact Management: Stores names, emails, phone numbers, company details
- ✅ Interaction Tracking: Logs calls, emails, meetings, and support tickets
- ✅ Sales Pipeline Management: Tracks leads through qualification, proposal, and closing stages
- ✅ Task & Activity Management: Assigns follow-ups, reminders, and action items
- ✅ Reporting & Analytics: Generates sales forecasts, performance dashboards, and conversion metrics
- ✅ Workflow Automation: Automates repetitive tasks like lead assignment and email sequences
Who Uses CRMs?
CRMs are essential for customer-facing teams:
- Sales Teams: To manage pipelines, track deals, and close revenue
- Customer Support: For ticket management and service history
- Marketing: To nurture leads and track campaign attribution
- Account Management: To maintain ongoing customer relationships
CDP vs CRM: The Core Differences Explained
While both platforms manage customer data, they serve fundamentally different purposes and operate in distinct ways.
| Feature | Customer Data Platform (CDP) | Customer Relationship Management (CRM) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Unified customer behavior & journey | Individual customer interactions |
| Data Collection | Automated via APIs, code, integrations | Manual entry by sales/support teams |
| Data Type | First-party, second-party, third-party data | Contact info, sales history, support logs |
| Users | Marketing, Product, Analytics, Leadership | Sales, Customer Support, Marketing |
| Use Cases | Personalization, segmentation, analytics | Lead management, sales tracking, support |
| Data Scope | All touchpoints across entire lifecycle | Direct customer-facing interactions only |
| Update Frequency | Real-time | Manual/periodic updates |
| Integration | Orchestrates data flow across tech stack | Standalone or limited integrations |
The Key Distinction: Behavior vs. Interactions
The fundamental difference boils down to this:
CDPs track customer behavior across all touchpoints—website visits, product usage, email engagement, social media interactions, in-app actions, and offline purchases. They answer questions like: What content does this segment consume? Which products are they interested in? When are they most engaged?
CRMs manage customer interactions with your team—sales calls, support tickets, email exchanges, and meeting notes. They answer questions like: When did we last contact this lead? What objections did they raise? What’s the status of their support request?
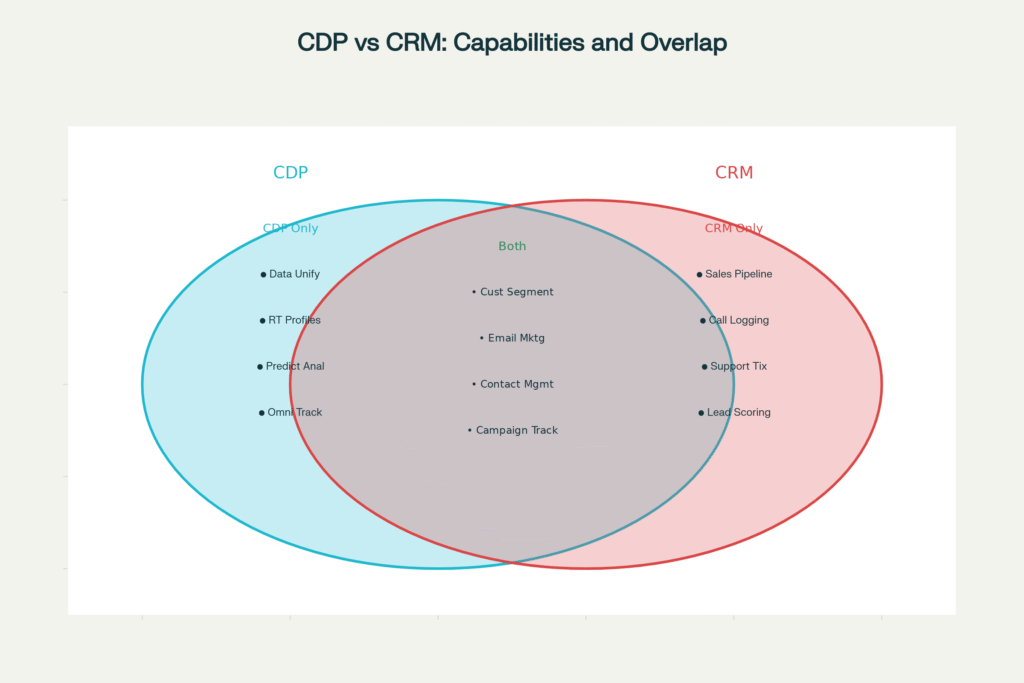
Visual representation of unique and overlapping capabilities between CDP and CRM systems, highlighting how both platforms complement each other.
Think of it this way: A CDP tells you what customers do, while a CRM tells you what your team does with customers. Both perspectives are critical for delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Data Collection: Automated vs. Manual
CDP Data Collection:
CDPs automatically capture data through:
- JavaScript tracking on websites and web apps
- Mobile SDKs for iOS and Android applications
- Server-side APIs from backend systems
- Pre-built connectors to SaaS tools (analytics, advertising, email platforms)
- Webhooks and event streams for real-time data ingestion
This automated collection means CDPs can process millions of events per day without manual intervention, creating a complete picture of customer behavior across channels.
CRM Data Collection:
CRMs rely primarily on manual data entry:
- Sales reps logging call notes after customer conversations
- Support agents creating tickets when customers report issues
- Marketers importing contact lists from events or campaigns
- Forms that require submission to capture information
While modern CRMs offer some automation (like email tracking or form integrations), the core data—contextual notes, qualitative feedback, relationship history—requires human input to capture properly.
The Market Landscape: Growth and Adoption Trends
The CDP and CRM markets are both experiencing significant growth, but at dramatically different scales and rates.
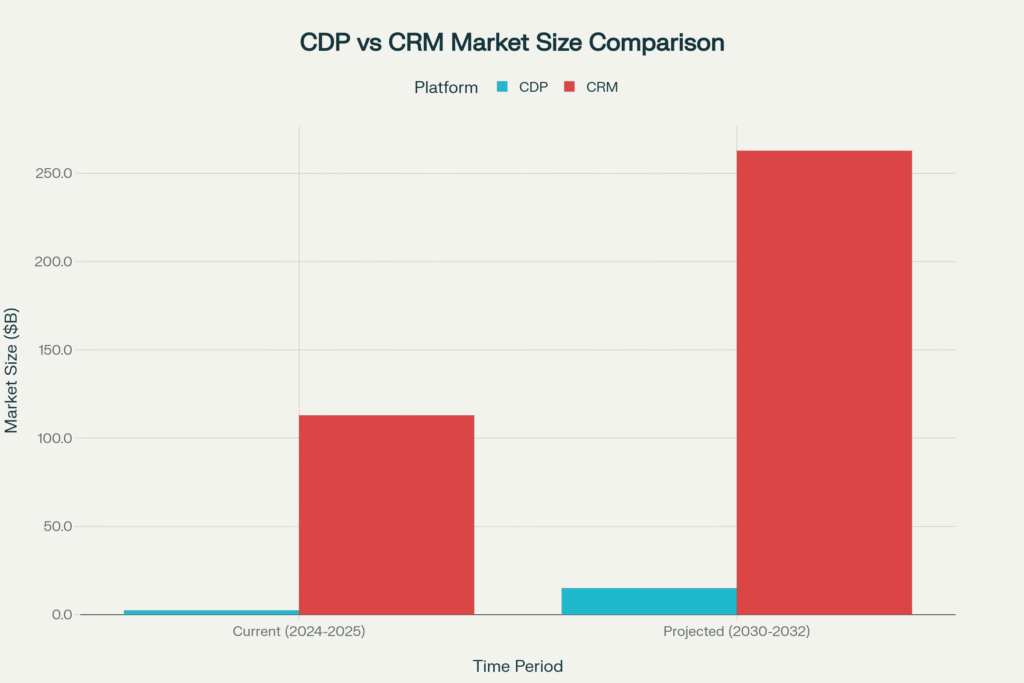
Market size comparison showing CDP’s explosive growth rate (24-40% CAGR) versus CRM’s steady expansion (12.8% CAGR) through 2032.
CDP Market: Explosive Growth
The CDP market is experiencing explosive expansion driven by several key factors:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| 2024 Market Size | $2.4B – $6.24B (varies by source) |
| 2030 Projected Size | $15B+ |
| CAGR (2024-2030) | 24.4% – 39.9% |
| Employment Growth (2024) | +3.4% (strongest since 2022) |
| Organic Growth Rate (Composable CDPs) | 12.9% |
Key Growth Drivers:
📊 Cookie Deprecation: Third-party cookie phase-out accelerating first-party data strategies
🔒 Privacy Regulations: GDPR, CCPA, and emerging laws requiring better data governance
🤖 AI Integration: Machine learning capabilities for predictive analytics and personalization
☁️ Cloud Adoption: Scalable cloud-based solutions enabling rapid deployment
📱 Omnichannel Expectations: Customers demanding consistent experiences across channels
CRM Market: Steady Expansion
The CRM market remains the larger, more mature market:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| 2025 Market Size | $112.91B |
| 2032 Projected Size | $262.74B |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 12.8% |
| Companies (10+ employees) Using CRM | 91% |
| Cloud-based CRM Adoption | 87% (up from 12% in 2008) |
| AI in CRM Market (2025) | $11.04B |
| Mobile CRM Market (2025) | $31.61B |
Key Growth Drivers:
🤖 AI-Powered Features: Predictive lead scoring, conversation intelligence, automated workflows
📱 Mobile-First Design: Field sales and remote work driving mobile CRM adoption
🔗 Integration Ecosystems: Seamless connections with marketing automation, communication tools
💡 Sales Enablement: Advanced analytics, forecasting, and revenue intelligence
Market Insight: While CRM is the larger market by revenue, CDP is growing 2-3x faster, reflecting the shift toward data-driven marketing and personalized customer experiences.
When to Use CDP vs CRM: Practical Decision Framework
Choosing between CDP and CRM depends on your specific business objectives and use cases.
| Scenario | Best Solution | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Unifying data from multiple sources | CDP | Automated data integration from all touchpoints |
| Managing sales pipeline | CRM | Specialized sales workflow management |
| Real-time personalization | CDP | Real-time profile updates and activation |
| Tracking customer support tickets | CRM | Interaction tracking and case management |
| Audience segmentation for campaigns | CDP | Behavioral data enables precise targeting |
| Nurturing individual leads | CRM | Detailed interaction history per contact |
| Predictive analytics & AI insights | CDP | Unified data enables ML model training |
| Recording sales call notes | CRM | Manual entry of context-specific information |
| Cross-channel behavior analysis | CDP | Tracks behavior across website, app, offline |
| Managing customer relationships | CRM | Focuses on building personal connections |
Use CDP When You Need:
1. Comprehensive Customer Understanding
A retail brand wants to understand the complete customer journey from first website visit through multiple purchases. A CDP automatically collects:
- Website browsing behavior (products viewed, time spent)
- Email engagement (opens, clicks, conversions)
- Mobile app usage (features used, session frequency)
- In-store purchases (via POS system integration)
- Loyalty program activity (points earned, rewards redeemed)
This unified view reveals patterns impossible to see in siloed systems.
2. Advanced Segmentation & Personalization
An e-commerce company segments customers based on:
- RFM analysis: Recency, Frequency, Monetary value
- Behavioral triggers: Cart abandonment, browse abandonment, repeat purchases
- Predictive scores: Churn likelihood, lifetime value, next purchase probability
- Interest categories: Inferred from browsing and purchase patterns
These dynamic segments update in real-time as customer behavior changes, enabling hyper-relevant marketing.
3. Omnichannel Campaign Orchestration
A travel company delivers coordinated experiences:
- Retarget website visitors with social media ads for destinations they explored
- Send personalized email recommendations based on search history
- Display mobile app notifications about price drops on saved trips
- Provide SMS updates on booking status and travel reminders
All channels pull from the same unified customer profile, ensuring message consistency.
Use CRM When You Need:
1. Sales Pipeline Management
A B2B software company tracks each opportunity through stages:
- Lead: Initial contact, qualification criteria assessed
- Opportunity: Demo scheduled, needs identified
- Proposal: Pricing presented, decision-makers engaged
- Negotiation: Contract terms discussed, objections addressed
- Closed-Won/Lost: Deal outcome recorded with win/loss analysis
Sales reps see complete history, next steps, and deal value at a glance.
2. Customer Support Excellence
A SaaS company’s support team uses CRM to:
- Track tickets from submission through resolution
- View complete history of previous support interactions
- Identify patterns in common issues for proactive solutions
- Measure satisfaction through post-resolution surveys
- Escalate complex cases with full context to senior agents
Every support interaction is documented, ensuring continuity across team members.
3. Relationship Building & Account Management
A consulting firm maintains long-term client relationships:
- Document meetings with detailed notes on discussions and decisions
- Track project milestones and deliverable schedules
- Identify upsell opportunities based on client growth and needs
- Manage renewals with automated reminders and proposal tracking
- Coordinate team handoffs with complete context preservation
The personal touch enabled by detailed relationship history differentiates service quality.
The Power of Integration: CDP + CRM Together
While CDPs and CRMs serve different purposes, their true power emerges when integrated. According to industry research, 92% of businesses acknowledge CRM’s crucial role in achieving revenue goals, and CDPs amplify this impact by enriching CRM data with behavioral insights.
How Integration Delivers Value
Customer Data Platform dashboard showing profiles, segments, records, and device analytics
| Benefit Area | How CDP + CRM Integration Delivers Value |
|---|---|
| Data Enrichment | CDP behavioral data enriches CRM contact records with website activity, product interests, engagement patterns |
| Sales Enablement | Sales reps see real-time intent signals (pages viewed, content downloaded) to prioritize hot leads |
| Marketing Effectiveness | Marketing campaigns leverage CRM purchase history + CDP behavioral data for hyper-personalization |
| Customer Experience | Unified view ensures consistent messaging across sales calls, marketing emails, support interactions |
| Operational Efficiency | Eliminates manual data transfer; automated syncing reduces errors and saves time |
| Revenue Impact | Companies report20-35% conversion increasesand50% faster lead-to-close cycles |
Real-World Integration Success Stories
Case Study 1: Fashion Retailer’s Personalization Win
A global fashion brand integrated their CDP (tracking online and in-store behavior) with Salesforce CRM (managing customer relationships). Results:
- 35% increase in conversions from personalized product recommendations
- 20% higher repeat purchases through targeted email campaigns
- 50% reduction in cart abandonment via real-time behavioral triggers
How it worked: The CDP identified customers browsing specific product categories. This data flowed to the CRM, triggering personalized email campaigns featuring those products plus complementary items based on purchase history. Sales teams also received alerts when high-value customers visited the website, enabling timely outreach.
Case Study 2: SaaS Company’s Sales Acceleration
A B2B SaaS company connected their CDP behavioral tracking with HubSpot CRM. Results:
- 50% reduction in lead-to-close time through better lead prioritization
- 25% increase in demo conversion rates via contextual sales conversations
- $2M additional ARR from identifying and engaging high-intent leads
How it worked: The CDP tracked which product pages prospects visited, which features they explored in free trials, and which content they downloaded. This intent data synced to CRM, automatically scoring leads and alerting sales reps when prospects showed high-interest signals. Sales calls became consultative conversations addressing specific needs rather than generic pitches.
Case Study 3: Retailer’s Churn Reduction
An online retailer integrated CDP analytics with their customer service CRM. Results:
- Reduced customer churn by identifying disengaged customers early
- Automated retention campaigns based on behavioral triggers
- Improved customer lifetime value through proactive engagement
How it worked: The CDP detected signals like decreased purchase frequency, reduced website visits, or negative sentiment in reviews. These insights triggered CRM workflows: personalized win-back offers, proactive support outreach, or targeted engagement campaigns before customers churned.
Implementation Strategy: Getting Started Right
Successfully implementing CDP and CRM systems—especially together—requires strategic planning and systematic execution.
Step 1: Assessment Phase
Audit Your Current Data Infrastructure
Before selecting platforms, understand your existing data landscape:
Questions to Answer:
- 🔍 What systems currently hold customer data? (Website analytics, email platform, POS, support desk, etc.)
- 🔍 How does data flow between these systems? (Manual exports, APIs, no connection?)
- 🔍 What’s the quality of your data? (Accuracy, completeness, consistency?)
- 🔍 Where are the data silos? (Marketing can’t see sales data? Product team isolated from support?)
- 🔍 What security and compliance requirements apply? (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, industry-specific regulations?)
Common Findings:
- Customer data scattered across 8-15 different systems
- 30-40% of data contains errors (duplicates, outdated information, formatting inconsistencies)
- Limited visibility across departments into customer journey
- Manual processes consuming significant team time for data manipulation
Step 2: Planning Phase
Define Clear Goals and Use Cases
Don’t implement technology for technology’s sake. Start with specific business objectives:
CDP Goals Might Include:
- ✅ Create unified customer profiles consolidating online and offline data
- ✅ Enable real-time personalization across website, email, and mobile app
- ✅ Build predictive models for churn, lifetime value, and next-best action
- ✅ Improve marketing attribution across channels
- ✅ Ensure privacy compliance while maximizing data utility
CRM Goals Might Include:
- ✅ Increase sales pipeline visibility and forecast accuracy
- ✅ Reduce lead response time through automated assignment
- ✅ Improve customer support resolution times and satisfaction scores
- ✅ Track account health for proactive relationship management
- ✅ Enable better collaboration between sales, support, and success teams
Integration Goals Might Include:
- ✅ Enrich CRM contacts with behavioral data from CDP
- ✅ Trigger marketing campaigns based on CRM sales stages
- ✅ Provide sales teams with real-time intent signals
- ✅ Create closed-loop reporting connecting marketing spend to revenue
- ✅ Deliver consistent experiences across all customer touchpoints
Choose Platforms with Strong Integration Capabilities
Not all CDPs and CRMs integrate equally well. Prioritize:
- Native integrations between selected platforms (e.g., Salesforce CDP + Salesforce CRM, Segment + HubSpot)
- Pre-built connectors to your essential tools
- Open APIs for custom integration needs
- Real-time sync capabilities (not just batch updates)
- Bi-directional data flow (not just one-way push)
Step 3: Integration Phase
Map Data Flows Between Systems
Document precisely how data should move:
Example Data Flow Map:
- Customer visits website → CDP captures behavior
- Customer fills form → CDP creates profile + pushes to CRM as lead
- Sales rep qualifies lead → CRM updates status
- CDP receives status update → Triggers nurture email sequence
- Customer engages with email → CDP tracks engagement + updates CRM
- Sales rep sees engagement → CRM triggers follow-up task
- Customer makes purchase → CRM records revenue + CDP updates segment
- CDP identifies upsell opportunity → Creates task in CRM for account manager
This mapping ensures every touchpoint is captured and every team has the data they need.
Implement Real-Time Sync Capabilities
Batch updates (syncing once daily) create stale data. Modern integrations should offer:
- Event-based triggers: Actions in one system instantly update the other
- Webhook connections: Real-time notifications of data changes
- API-first architecture: Continuous data streaming
- Conflict resolution: Clear rules for handling discrepancies
Common Integration Approaches:
- Native integrations: Built-in connectors (simplest, fastest)
- iPaaS solutions: Integration Platform as a Service like Zapier, Workato, Alumio (flexible, code-light)
- Custom APIs: Direct system-to-system connections (most control, requires development)
- ETL tools: Extract, Transform, Load for complex data transformations
Step 4: Activation Phase
Train Teams on Unified Data Access
Technology alone doesn’t drive results—people do. Comprehensive training ensures adoption:
For Marketing Teams:
- How to create segments using behavioral and CRM data
- Building multi-channel campaigns activated through CDP
- Interpreting unified analytics and attribution reports
- Best practices for data governance and consent management
For Sales Teams:
- Accessing behavioral insights within CRM interface
- Interpreting intent signals and engagement scores
- Using data to prioritize outreach and personalize conversations
- Documenting interactions that feed back to CDP
For Support Teams:
- Viewing complete customer history (purchases, interactions, issues)
- Identifying at-risk customers through behavioral signals
- Escalating complex cases with full context
- Contributing feedback that improves customer journey mapping
For Leadership:
- Dashboard access for strategic metrics (CAC, LTV, churn rate, etc.)
- Understanding data flows and system architecture
- Making data-driven decisions based on unified insights
- Ensuring governance and compliance
Launch Pilot Campaigns
Start small to validate integration and build confidence:
Example Pilot 1: Sales Enablement
- Objective: Reduce lead response time by 50%
- Approach: CDP identifies website visitors who view pricing pages, instantly creates/updates CRM lead with “high intent” flag
- Measurement: Track time from website visit to sales outreach, conversion rate of high-intent leads
- Duration: 4-6 weeks
Example Pilot 2: Personalized Email
- Objective: Increase email conversion rate by 25%
- Approach: Segment customers in CDP based on purchase history + browsing behavior, send targeted product recommendations
- Measurement: Open rate, click rate, conversion rate, revenue per email
- Duration: 3-4 campaigns (6-8 weeks)
Example Pilot 3: Churn Prevention
- Objective: Reduce monthly churn by 15%
- Approach: CDP identifies behavioral churn signals (reduced engagement), creates CRM tasks for account managers to reach out proactively
- Measurement: Churn rate of targeted accounts vs. control group, customer satisfaction scores
- Duration: 8-12 weeks
Step 5: Optimization Phase
Monitor Data Quality Continuously
Data degrades over time without active management:
Data Quality Metrics to Track:
- Completeness: % of records with all required fields populated
- Accuracy: % of records verified as correct (via validation checks, user confirmation)
- Consistency: % of records matching across systems
- Timeliness: Average lag between event occurrence and data availability
- Uniqueness: % of duplicate records identified and resolved
Best Practices:
- Automated validation rules: Reject invalid data at entry point
- Regular audits: Monthly data quality reviews
- Deduplication processes: Merge duplicate records based on matching rules
- Data enrichment: Append missing information from third-party sources
- Sunset policies: Archive or delete outdated records
Measure ROI and Iterate
Quantify the impact of your CDP and CRM integration:
Financial Metrics:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Has more targeted marketing reduced CAC?
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Are personalized experiences increasing CLV?
- Conversion Rates: Are behavioral insights improving conversions?
- Revenue Attribution: Can you tie marketing spend to closed revenue?
- Efficiency Gains: How much time saved on manual data tasks?
Operational Metrics:
- Lead Response Time: How quickly do sales reps engage hot leads?
- Campaign Performance: Are segmented campaigns outperforming generic blasts?
- Data Accessibility: Are teams finding data when they need it?
- System Adoption: Are teams actively using both platforms?
Customer Experience Metrics:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Is customer satisfaction improving?
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Are experiences becoming easier?
- Churn Rate: Are you retaining customers better?
- Repeat Purchase Rate: Are customers coming back more frequently?
Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Data Silos Persist
Problem: Even with CDP and CRM, data remains fragmented if integration is incomplete.
Symptoms:
- Marketing can’t see which leads converted to customers
- Sales lacks visibility into website engagement and email interactions
- Support doesn’t know purchase history or product usage
Solutions:
✅ Establish single source of truth: Define which system owns each data type
✅ Map all data flows: Document every integration point and data exchange
✅ Implement data governance: Clear policies on data ownership, quality, access
✅ Use iPaaS if needed: Integration platforms bridge systems that don’t natively connect
Challenge 2: Integration Complexity
Problem: Technical challenges syncing data between systems with different structures.
Symptoms:
- Data mismatches between systems
- Sync delays causing stale information
- Conflicting records creating confusion
Solutions:
✅ Choose systems with pre-built integrations: Reduces custom development
✅ Map data structures early: Align field names, formats, definitions before integration
✅ Leverage AI-powered mapping: Modern tools automate field matching
✅ Implement clear conflict resolution rules: Define which system wins for each data type
Challenge 3: User Adoption Resistance
Problem: Teams continue using old processes instead of embracing new systems.
Symptoms:
- Low login rates and feature usage
- Continued reliance on spreadsheets
- Complaints about system complexity
- Data quality issues from inconsistent use
Solutions:
✅ Demonstrate value quickly: Show how systems make jobs easier
✅ Provide comprehensive training: Role-specific instruction with real scenarios
✅ Create champions: Identify power users in each department to advocate
✅ Simplify interfaces: Customize views to show only relevant data
✅ Gather feedback: Regular check-ins to address pain points
Challenge 4: Privacy and Compliance Concerns
Problem: Managing customer data across systems while meeting regulatory requirements.
Symptoms:
- Uncertainty about data retention policies
- Difficulty fulfilling data access/deletion requests
- Inconsistent consent management
- Risk of regulatory fines
Solutions:
✅ Centralize consent management: CDP tracks preferences across all touchpoints
✅ Implement data governance framework: Clear policies, documented processes, assigned accountability
✅ Use privacy-native features: Data masking, role-based access controls, automated deletion
✅ Regular compliance audits: Periodic reviews ensuring adherence to regulations
The Future: Emerging Trends in CDP and CRM
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Both CDPs and CRMs are increasingly leveraging AI:
CDP AI Applications:
- Predictive analytics: Churn probability, lifetime value forecasting, next-best action recommendations
- Intelligent segmentation: AI-discovered segments based on hidden patterns
- Content personalization: Dynamic content selection optimized for each individual
- Journey orchestration: AI-determined optimal channel, timing, and message
CRM AI Applications:
- Conversational intelligence: Call transcription, sentiment analysis, coaching insights
- Predictive lead scoring: AI-calculated likelihood to convert
- Smart forecasting: Revenue predictions based on historical patterns
- Automated data entry: AI extracts information from emails, calls, and documents
The AI in CRM market alone is expected to reach $11.04 billion in 2025, highlighting the rapid adoption of intelligent features.
Composable CDPs (building CDP functionality from existing data warehouse infrastructure) are gaining traction:
- 12.9% organic growth rate for composable CDP vendors (vs. 3.4% for packaged CDPs)
- Lower implementation costs by leveraging existing investments
- Greater flexibility to customize data models and workflows
- Better suited for mature data teams with engineering resources
This trend reflects organizations seeking more control over their data architecture.
3. Real-Time Everything
The expectation for real-time experiences is becoming non-negotiable:
- Instant personalization: Website content adapting as users browse
- Real-time triggers: Immediate actions based on customer behavior
- Live dashboards: Up-to-the-second reporting for decision-making
- Streaming data: Continuous flow replacing batch processing
Modern CDPs and CRMs must support millisecond-latency data updates to meet these expectations.
4. Privacy-First Architecture
With cookie deprecation and stricter regulations:
- First-party data strategies becoming essential
- Zero-party data (explicitly shared by customers) growing in importance
- Privacy-enhancing technologies (differential privacy, federated learning) emerging
- Transparent data practices as competitive differentiator
CDPs with robust consent management and data governance capabilities will be table stakes.
5. B2B and B2C Convergence
Modern CDPs are breaking down barriers between consumer and business customer understanding:
- Unified platforms supporting both B2C and B2B use cases
- Account-based profiles for B2B complementing individual profiles
- Buying group insights showing how multiple stakeholders influence decisions
- Seamless switching between consumer and professional contexts
This convergence enables consistent strategies across different customer types.
Making the Decision: CDP, CRM, or Both?
Start with CRM If:
✅ Your primary need is managing sales and support relationships
✅ You have limited data infrastructure (CRM is simpler to implement)
✅ Your team is small (under 50 people) and needs core relationship management
✅ Budget is constrained (CRMs generally have lower starting costs)
✅ You’re in early growth stages (build relationship foundation first)
Recommended Path: Implement CRM first, establish solid customer relationship practices, then add CDP as you scale and need more sophisticated marketing.
Start with CDP If:
✅ Your primary need is understanding customer behavior across channels
✅ You have complex data infrastructure to unify
✅ Marketing personalization is critical to your business model
✅ You operate in e-commerce/digital-first where behavioral data is rich
✅ You’re facing privacy compliance challenges requiring data centralization
Recommended Path: Implement CDP to establish data foundation, then integrate CRM to layer on relationship management capabilities.
Implement Both If:
✅ You’re experiencing rapid growth requiring sophisticated operations
✅ You have both complex marketing and sales operations
✅ Your customer journey spans multiple touchpoints and channels
✅ You can invest in integration and change management
✅ You want closed-loop reporting connecting marketing to revenue
Recommended Path: Implement sequentially (CRM first for most B2B, CDP first for most B2C), then integrate. Alternatively, choose platforms from same vendor for easier integration (e.g., Salesforce CDP + Salesforce CRM, Adobe Experience Platform + Microsoft Dynamics).
Conclusion: The Future is Unified Customer Data
The debate of CDP vs CRM misses the fundamental point: modern customer experience requires both behavioral insights and relationship management. According to industry research, 72% of marketers use CDPs alongside other tools, recognizing that no single platform solves every need.
Key Takeaways
1. They Serve Different Purposes
- CDPs unify customer behavior data across all touchpoints for marketing personalization
- CRMs manage customer relationships and interactions for sales and support
- Both are essential for comprehensive customer understanding
2. Integration Amplifies Value
- CDP + CRM integration delivers 20-35% conversion increases
- 50% faster lead-to-close cycles when sales teams have behavioral insights
- Unified data eliminates silos and creates seamless customer experiences
3. The Market is Growing Rapidly
- CDP market growing 24-40% annually (vs. CRM’s 12.8%)
- 91% of companies with 10+ employees use CRM
- CDP adoption accelerating due to cookie deprecation and privacy regulations
4. Implementation Requires Strategy
- Start with clear goals and use cases
- Assess data infrastructure before selecting platforms
- Prioritize platforms with strong integration capabilities
- Invest in training and change management
- Monitor data quality continuously
5. The Future is AI-Powered and Real-Time
- AI transforming both CDPs (predictive analytics) and CRMs (conversational intelligence)
- Real-time data processing becoming standard expectation
- Privacy-first architecture essential as regulations tighten
- Composable approaches offering greater flexibility for mature organizations
Your Next Steps
Immediate Actions:
- Audit your current customer data landscape
- What systems hold customer information?
- Where are the data silos?
- What’s your data quality like?
- Define your primary use cases
- Is your biggest need sales pipeline management or marketing personalization?
- Which problems cost you the most revenue today?
- Evaluate platform options
- Research vendors that serve your specific needs
- Prioritize integration capabilities
- Request demos focused on your use cases
- Calculate potential ROI
- Quantify cost of current inefficiencies
- Estimate impact of better customer understanding
- Model revenue improvements from personalization and better conversion
- Start with a pilot
- Choose high-impact, manageable scope
- Measure results rigorously
- Scale based on proven success
The Bottom Line
In 2025 and beyond, customer data is your most valuable asset. The question isn’t whether to invest in CDP or CRM—it’s how to leverage both to create competitive advantage through superior customer understanding and experiences.
Organizations that successfully unify behavioral data (CDP) with relationship data (CRM) will deliver the personalized, seamless experiences customers demand while empowering their teams with the insights needed to drive growth.
The future belongs to companies that transform customer data from scattered information into strategic intelligence. Start your journey today.
Comments