The utility sector stands at the precipice of a revolutionary transformation. As global energy demands surge and aging infrastructure strains under mounting pressure, predictive analytics has emerged as a critical technology reshaping how utility companies operate, maintain assets, and serve customers.
By harnessing the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze vast streams of data from smart meters, IoT sensors, and historical records, utilities can now anticipate equipment failures, optimize resource allocation, and deliver unprecedented levels of service reliability.
This comprehensive exploration examines how predictive analytics is revolutionizing the utility industry, driving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling the transition toward sustainable energy systems.
The Market Opportunity: Why Now?
The numbers tell a compelling story. The global utility analytics market is experiencing explosive growth, driven by technological advancement and operational necessity.
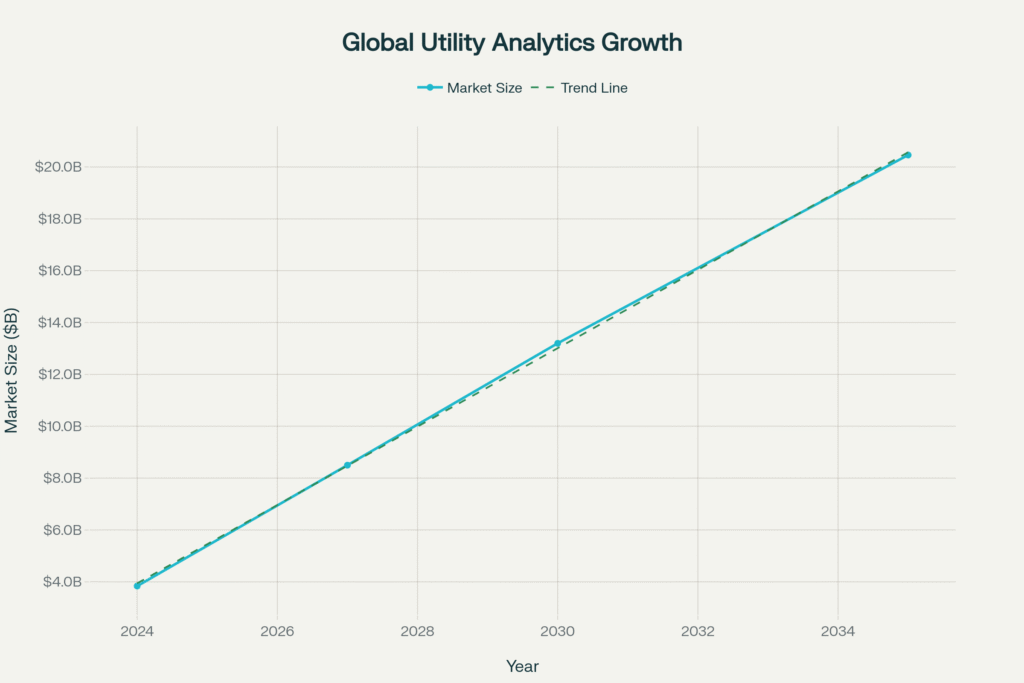
Projected growth trajectory of the global utility analytics market from 2024 to 2035, showing a compound annual growth rate of 16.43%
Key Market Drivers
- Rising Energy Demand: Electricity consumption projected to increase 46% cumulatively through 2032
- Aging Infrastructure: Critical equipment approaching end-of-life requiring strategic replacement
- Renewable Integration: One-third of global electricity from renewables by 2025, requiring sophisticated forecasting
- Digital Transformation: Over 1.06 billion smart meters installed globally, generating unprecedented data volumes
- Cost Pressures: Unplanned downtime costing utilities an average of $260,000 per hour
| Market Segment | 2024 Value | Projected (2030-2035) | Growth Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Utility Analytics Market | $3.84 Billion | $20.46 Billion (2035) | AI/ML adoption, Smart grid deployment |
| Utilities Data Analytics Market | $9.7 Billion | $24.8 Billion (2033) | IoT integration, Cloud platforms |
| Smart Meter Installations | 1.06 Billion Units | 1.75 Billion Units (2030) | Government mandates, Digital transformation |
| Energy & Utility Analytics CAGR | N/A | 16.43% | Renewable energy, Grid modernization |
Understanding Predictive Analytics in Utilities
What Is Predictive Analytics?
Predictive analytics in utilities encompasses the systematic application of statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and data mining techniques to forecast future events, behaviors, and trends based on historical and real-time data.
Unlike traditional business intelligence that explains what happened, predictive analytics answers the critical question: what will happen next?
The Three Pillars of Predictive Analytics
1. Comprehensive Data Collection
Modern utilities collect data from multiple sources:
- Smart Meters: Granular consumption data at 15-minute to real-time intervals
- IoT Sensors: Temperature, vibration, pressure, current, and environmental monitoring
- SCADA Systems: Real-time operational data from grid infrastructure
- Weather Stations: Temperature, humidity, wind speed for demand forecasting
- Historical Records: Years of maintenance logs and equipment performance data

High-voltage electrical substation with large power transformer equipment outdoors
2. Advanced Analytical Techniques
The technology stack powering predictive analytics includes:
| Technology Layer | Key Technologies | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Smart Meters, IoT Sensors, SCADA Systems | Real-time monitoring & data capture |
| Data Processing | Edge Computing, Cloud Platforms, Data Lakes | Data cleaning, transformation, storage |
| Analytics & ML | Python/R, TensorFlow, Random Forest, Neural Networks | Predictive models, forecasting, anomaly detection |
| Visualization | Power BI, Tableau, Grafana, Custom Dashboards | Operational insights, reporting, alerts |
| Integration | APIs, Middleware, ETL Pipelines, Data Fabric | System connectivity, data flow |
Machine Learning Techniques
- Regression Models: Establish relationships between variables (e.g., temperature and demand)
- Time-Series Analysis: Capture temporal patterns and seasonality using ARIMA models
- Random Forest: Handle non-linear relationships in complex datasets
- Neural Networks: Model intricate system behaviors with deep learning
- Ensemble Methods: Combine multiple models for enhanced accuracy
3. Actionable Insights
Analytics outputs drive concrete operational decisions:
- Automated Alerts: Trigger maintenance before equipment failure
- Optimized Scheduling: Balance supply and demand in real-time
- Strategic Planning: Inform long-term infrastructure investments
- Customer Engagement: Personalize communications and services
The Maintenance Revolution: From Reactive to Predictive
The most impactful application of predictive analytics lies in asset maintenance. Traditional approaches are costly and inefficient compared to data-driven strategies.
Comparing Maintenance Strategies
| Maintenance Type | Approach | Cost | Downtime | Equipment Life | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactive Maintenance | Fix after failure | Highest (3-5x) | Unplanned & lengthy | Shortest | Low (~55%) |
| Preventive Maintenance | Schedule-based intervals | Moderate | Planned but frequent | Moderate | Medium (~65%) |
| Predictive Maintenance | Data-driven insights | Lowest (8-12% savings) | Minimal & planned | Longest (20-40% extension) | High (85-90%) |
The Predictive Maintenance Advantage
How It Works:
Continuous monitoring of equipment through sensors captures:
- Vibration patterns indicating bearing wear
- Thermal signatures revealing insulation degradation
- Oil analysis showing contamination levels
- Electrical signatures detecting winding faults
- Acoustic patterns identifying mechanical issues
Machine learning models analyze these data streams to:
- Predict failures 5-7 days in advance for critical components
- Forecast degradation 2-4 weeks ahead for gradually failing systems
- Optimize timing for maintenance interventions
- Prioritize resources based on failure probability and impact
Real-World Impact: Case Studies
Duke Energy partnered with Microsoft and Accenture to develop an AI-driven platform using Azure and Dynamics 365. The system integrates satellite and ground sensor data for real-time leak detection in natural gas pipelines, helping Duke Energy progress toward net-zero methane emissions by 2030.
Siemens Energy created digital twins for heat recovery steam generators that predict corrosion patterns, potentially saving utilities $1.7 billion annually by reducing inspection needs and downtime by 10%.
AES Corporation deployed H2O.ai’s predictive platform across wind turbines and smart meters, achieving $1 million in annual savings and a 10% reduction in customer outages by optimizing maintenance and predicting component failures.
Financial Impact: The ROI of Predictive Analytics
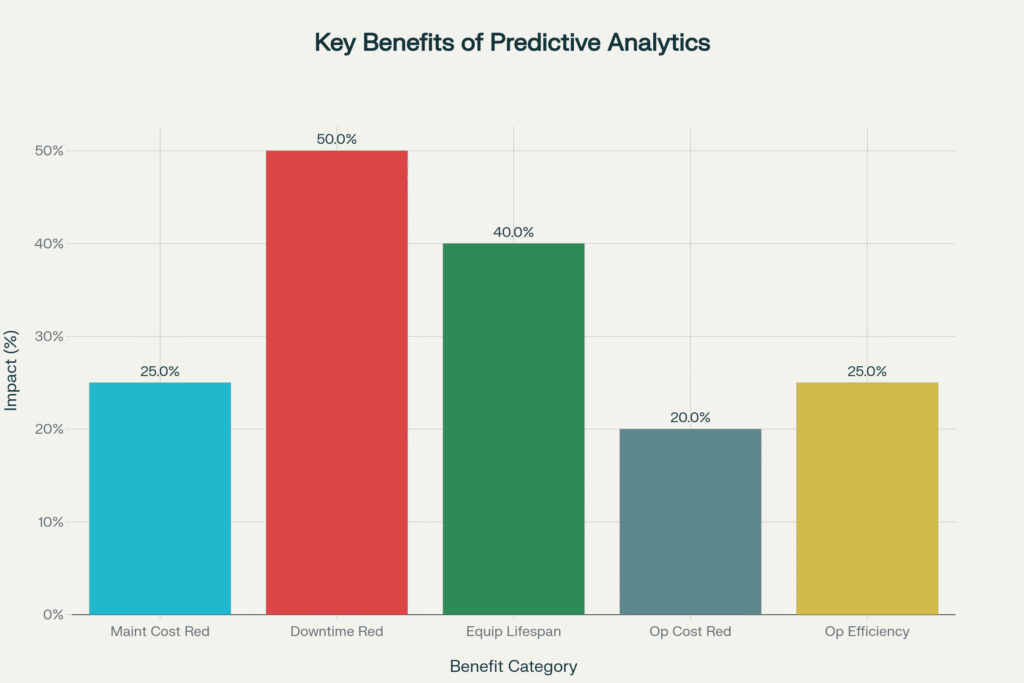
Financial and operational benefits delivered by predictive analytics implementation in utility companies, showing percentage improvements across key metrics
Direct Financial Benefits
| Benefit Category | Impact Range | Annual Value (Typical Utility) |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Cost Reduction | 18-25% | $2-3 Million |
| Unplanned Downtime Reduction | 30-50% | $5-8 Million |
| Equipment Lifespan Extension | 20-40% | $3-5 Million |
| Operational Cost Reduction | 15-20% | $1-2 Million |
| Operational Efficiency Increase | 25% | $4-6 Million |
| ROI Ratio (12-18 months) | 10:1 to 30:1 | $10-30 Million |
| Return per Dollar Invested | $9.01 per $1 | Varies |
Breaking Down the Savings
Maintenance Cost Reduction (18-25%)
- Eliminate 30% of unnecessary preventive maintenance tasks
- Reduce emergency repairs costing 3-5x more than planned work
- Optimize parts inventory based on predicted demand
- Decrease overtime labor through better scheduling
Downtime Prevention
- Manufacturing facilities experience 323 hours of annual unplanned downtime
- At $260,000 per hour average cost, a 30-50% reduction saves $2.5-4.2 million annually
- Critical utility operations face even higher downtime costs
Asset Life Extension
- Extend equipment lifespan by 20-40% through optimized maintenance timing
- Delay capital expenditures for replacements
- Maximize return on asset investments
- Reduce environmental impact from manufacturing and disposal
Payback Timeline
Organizations implementing predictive analytics typically see:
- 95% report positive returns
- 27% achieve full payback within 12 months
- Majority reach payback in 12-18 months
- 10:1 to 30:1 ROI ratios sustained long-term
Transformative Applications Across Operations
1. Energy Demand Forecasting and Load Optimization
The Challenge: Balancing supply and demand in real-time while minimizing costs and emissions.
The Solution: AI-powered forecasting integrates multiple data streams:
Data Inputs:
- Weather forecasts (temperature, humidity, wind)
- Historical consumption patterns
- Real-time smart meter data
- Calendar information (holidays, events)
- Economic indicators
- Renewable generation forecasts
Accuracy Improvements:
Operational Benefits:
- Optimize generation scheduling across diverse resources
- Reduce reliance on expensive peaking plants
- Minimize spot market energy purchases
- Improve renewable energy utilization
- Reduce reserve margin requirements
Case Study: Google’s neural network for wind energy improved forecast accuracy, boosting financial returns by 20%. The system predicts wind power output 36 hours in advance, enabling optimal grid integration.
2. Smart Grid Management and Outage Prevention
Power outages cost U.S. businesses approximately $150 billion annually. Smart grid technology with predictive capabilities transforms grid reliability.
Key Applications:
Fault Detection & Prevention
- Continuous sensor data analysis identifies equipment anomalies
- Early warning systems alert operators to developing issues
- Predictive models forecast where outages are likely to occur
Load Balancing Optimization
- Real-time power distribution adjustments prevent overloads
- Dynamic routing reduces transmission losses
- Automated voltage regulation maintains power quality
Self-Healing Grid Capabilities
- Automatic power rerouting during outages
- Minimized customer impact through intelligent switching
- Faster restoration through precise fault location
Vegetation Management
- AI analysis of satellite/drone imagery identifies high-risk areas
- Predictive models forecast tree growth into power lines
- Optimized trimming schedules prevent vegetation-related outages
Case Study: Cisco’s grid modernization project with BC Hydro equipped the utility with a smart grid system that improved reliability and efficiency while supporting renewable energy integration, setting new standards for utility operations.
3. Customer Engagement and Personalized Services
Predictive analytics transforms the utility-customer relationship from transactional to interactive and personalized.
Customer-Centric Applications:
Consumption Forecasting
- Personalized bill projections enable better budgeting
- Early alerts for unusual consumption patterns
- Comparison with similar households
Usage Recommendations
- Identify opportunities for energy savings
- Appliance-level consumption insights
- Personalized efficiency tips
Dynamic Pricing Communication
- Optimal times to run appliances
- Cost savings from load shifting
- Real-time rate information
Proactive Outage Management
- Personalized notifications about service disruptions
- Accurate estimated restoration times
- Multi-channel communication (SMS, email, app)
Impact Metrics:
- Octopus Energy: AI-driven customer support achieved 80% satisfaction vs. 65% for human agents
- Smart meters: Provide 95-98% billing accuracy, minimizing disputes
- Informed customers: Reduce consumption by 5-15%
4. Renewable Energy Integration
The transition to renewable energy creates unprecedented forecasting challenges. Solar and wind generation varies with weather conditions, creating grid balancing complexities.
Predictive Analytics Solutions:
Generation Forecasting
- Weather-based solar irradiance predictions
- Wind speed and direction forecasting
- Cloud movement tracking for solar variability
- Seasonal pattern analysis
Grid Integration Optimization
- Real-time balancing of variable generation
- Energy storage charging/discharging decisions
- Conventional generation ramping coordination
- Transmission capacity management
Financial Optimization
- Renewable energy credit maximization
- Wholesale market bidding strategies
- Curtailment minimization
- Ancillary services participation
Results: With renewable energy projected to comprise one-third of global electricity by 2025, predictive analytics is essential for grid stability and economic viability.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
While predictive analytics offers transformative potential, utilities face significant hurdles.
Challenge 1: Data Quality and Integration
Common Issues:
- ❌ Siloed data across legacy systems
- ❌ Inconsistent formats and standards
- ❌ Incomplete historical records
- ❌ Inaccurate sensor readings
- ❌ OT/IT system disconnection
Solutions:
- ✅ Implement data governance frameworks
- ✅ Execute systematic data cleansing initiatives
- ✅ Deploy integration platforms (data fabric, APIs)
- ✅ Establish continuous quality monitoring
- ✅ Create unified data layers
Challenge 2: Legacy Infrastructure Constraints
Common Issues:
- ❌ Outdated SCADA systems lacking APIs
- ❌ Aging equipment without sensor support
- ❌ Legacy databases unable to handle real-time data
- ❌ Proprietary systems resisting integration
Solutions:
- ✅ Phased modernization approach
- ✅ Edge computing for local processing
- ✅ Middleware bridging legacy and modern systems
- ✅ Hybrid architectures leveraging existing investments
Challenge 3: Organizational and Cultural Barriers
Common Issues:
- ❌ Resistance to change from the traditional workforce
- ❌ Data science and analytics skills gaps
- ❌ Siloed organizational structures
- ❌ Risk-averse cultures are hesitant to trust algorithms
- ❌ Unclear roles and responsibilities
Solutions:
- ✅ Comprehensive training programs
- ✅ Cross-functional analytics teams
- ✅ Pilot projects demonstrating value
- ✅ Clear governance structures
- ✅ Cultural transformation initiatives
Challenge 4: Regulatory and Cybersecurity Concerns
Regulatory Challenges:
- Complex compliance requirements
- Unclear AI application guidance
- Capital vs. operating expense questions
- Data privacy regulations (CCPA, GDPR)
Cybersecurity Risks:
- Expanded attack surfaces from IoT devices
- Customer data breach potential
- Grid operation manipulation threats
- Cloud platform vulnerabilities
Mitigation Strategies:
- Network segmentation and isolation
- End-to-end encryption
- Multi-factor authentication
- Continuous threat monitoring
- Comprehensive incident response plans
- Regulatory engagement and compliance frameworks
Future Horizons: Emerging Trends
1. Autonomous Operations
The evolution toward self-managing utility infrastructure:
- Autonomous grid management makes real-time decisions
- Self-healing grids automatically restore service
- Robotic inspections using drones and robots with AI image analysis
- Automated dispatch optimizing field crew deployment
Example: Duke Energy uses AI-driven autonomous inspections with cameras and sensors analyzing data in real-time, reducing reliance on human workers while enhancing safety.
2. Digital Twins and Advanced Simulation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets:
Applications:
- Equipment degradation simulation under various conditions
- Grid response modeling for extreme weather
- Renewable integration impact assessment
- Maintenance strategy effectiveness testing
- Customer behavior scenario analysis
Example: Siemens Gamesa’s digital twin simulates offshore wind farm operations 4,000 times faster than real-time, optimizing turbine layouts and cutting energy costs.
3. Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics
Processing data at the network edge enables:
- Millisecond-latency responses for critical decisions
- Reduced bandwidth consumption to cloud
- Continued operation during connectivity disruptions
- Enhanced privacy by minimizing data transmission
Use Cases:
- Real-time grid balancing
- Substation protection decisions
- Smart meter anomaly detection
- Distributed energy resource coordination
4. Generative AI and Large Language Models
Emerging applications:
- Automated compliance and engineering report generation
- Natural language queries of operational data
- Maintenance troubleshooting chatbots for field personnel
- Synthetic data generation for model training
- Accelerated analytics application development
5. Quantum Computing for Optimization
Future potential for solving complex problems:
- Grid topology optimization
- Multi-resource generation scheduling
- Demand response across millions of devices
- Large-scale renewable integration management
While practical quantum computing remains years away, forward-thinking utilities are exploring quantum algorithms today.
Strategic Roadmap: Implementation Best Practices
Step 1: Start with High-Impact Use Cases
Recommended Starting Points:
- ✅ Predictive maintenance for critical assets (transformers, turbines)
- ✅ Short-term load forecasting for operational optimization
- ✅ Outage prediction for improved customer satisfaction
- ✅ Billing accuracy improvements through anomaly detection
Success Criteria:
- Measurable ROI within 12-18 months
- Clear operational metrics improvement
- Manageable technical complexity
- Strong stakeholder support
Step 2: Build a Solid Data Foundation
Critical Investments:
- Data governance frameworks and policies
- Data quality assessment and remediation
- Integration platforms (APIs, middleware, data fabric)
- Data catalogs for discovery and understanding
- Organization-wide data literacy programs
Remember: Poor data quality undermines model accuracy and leads to incorrect insights.
Step 3: Adopt Cloud-Native Architecture
Benefits of Cloud Deployment:
- Elastic scaling for variable workloads
- Access to latest AI/ML services
- Reduced capital expenditure
- Faster capability deployment
- Built-in security and compliance features
Market Evidence: Cloud-based deployment leads utility analytics growth with 16.7% CAGR.
Step 4: Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Key Actions:
- Establish analytics centers of excellence
- Create cross-functional project teams
- Define clear governance and decision rights
- Build communities of practice
- Align incentives for collaboration
Critical Success Factor: Analytics success requires collaboration across IT, operations, engineering, customer service, and executive leadership.
Step 5: Partner Strategically
Leverage External Expertise:
- Technology vendors for platforms and specialized capabilities
- Consulting firms for implementation experience
- Research institutions for cutting-edge methodologies
- Industry consortia for peer learning
Strategic partnerships accelerate implementation, reduce costs, and increase success probability.
Step 6: Measure and Communicate Value
Establish Clear Metrics:
Leading Indicators:
- Model accuracy and precision
- Data quality scores
- User adoption rates
- Process cycle time improvements
Lagging Indicators:
- Cost savings achieved
- Downtime reduction
- Customer satisfaction improvements
- Equipment lifespan extension
Communication Strategy:
- Create executive dashboards
- Share success stories broadly
- Quantify business impact
- Celebrate team achievements
Regular communication sustains executive commitment and resource allocation.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Predictive analytics represents far more than an incremental improvement—it constitutes a fundamental transformation in how utilities operate. The convergence of smart meters, IoT sensors, cloud computing, and advanced AI creates unprecedented opportunities to anticipate problems, optimize operations, and deliver superior service.
The Imperative for Action
Why Act Now:
📈 Market Growth: The global utility analytics market will grow from $3.84B (2024) to $20.46B (2035)—a 16.43% CAGR
💰 Proven ROI: Organizations achieve 10:1 to 30:1 returns within 12-18 months
⚡ Rising Demand: Electricity consumption projected to increase 46% by 2032
🌱 Renewable Integration: One-third of global electricity from renewables by 2025 requires sophisticated forecasting
🔧 Aging Infrastructure: Critical equipment approaching end-of-life demands strategic replacement
Success Requires a Holistic Approach
Technology alone doesn’t guarantee success. Utilities must:
- ✅ Invest in data quality and governance
- ✅ Modernize legacy infrastructure strategically
- ✅ Transform organizational culture
- ✅ Navigate evolving regulatory landscapes
- ✅ Build cross-functional capabilities
- ✅ Leverage strategic partnerships
The Competitive Divide
Forward-thinking utilities are already reaping benefits:
- Duke Energy: AI-driven pipeline inspections advancing net-zero goals
- AES Corporation: $1M annual savings, 10% outage reduction
- Octopus Energy: 80% customer satisfaction with AI support
These pioneers demonstrate that predictive analytics, thoughtfully implemented, delivers transformational value across operational, financial, and strategic dimensions.
Your Next Steps
The transformation is happening now. The question isn’t whether to adopt predictive analytics but how quickly and effectively you can implement it.
Recommended Actions:
- Assess current analytics maturity
- Identify high-impact pilot use cases
- Invest in data foundation and talent
- Partner with experienced vendors and consultants
- Execute pilot projects demonstrating value
- Scale successful initiatives across operations
- Measure and communicate results continuously
The path forward requires vision, investment, collaboration, and persistence—but the destination of a smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable utility sector justifies the journey.
Comments