Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has revolutionized how businesses automate repetitive tasks, with 53% of companies already implementing it and 78% planning or actively implementing RPA in their operations. Yet as automation technologies evolve, a more sophisticated approach called Intelligent Automation (IA) is emerging, combining RPA’s strengths with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities.
The critical question for organizations is no longer whether to automate, but which automation technology best addresses your specific business challenges. Understanding the differences between RPA and Intelligent Automation, when to use each, and how they work together is essential for building a successful automation strategy that drives digital transformation.
This comprehensive guide compares RPA and Intelligent Automation across all dimensions, from core capabilities and market growth to implementation strategies and real-world use cases. Whether you’re evaluating automation platforms, planning your first deployment, or scaling existing initiatives, this guide provides the insights needed to make informed decisions about your automation journey.
What Is RPA?
RPA Definition and Core Capabilities
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is technology that creates and deploys software robots (or “bots”) to automate repetitive, rule-based business processes. RPA bots work by mimicking human actions like clicking, typing, and data entry to interact with applications through their user interfaces (UIs) just as humans would.
Key RPA Characteristics:
- Rule-based Logic: Operates based on IF/THEN rules and predefined workflows
- Structured Data: Works effectively with consistent, formatted data inputs
- No Learning: Bots perform the same way every time without adapting
- Fast Implementation: Deployable within weeks to months
- Lower Initial Cost: Less complex than intelligent automation approaches
- Non-invasive: Works with existing systems without requiring integration changes
Common RPA Use Cases:
- Invoice Processing: Extract data from invoices, enter into ERP systems
- Data Entry: Transfer information between applications
- Report Generation: Compile and format data into standard reports
- Account Opening: Create accounts following predefined procedures
- Employee Onboarding: Fill forms, create accounts, send notifications
- Order Processing: Route orders, update inventory systems
- Claims Processing: Handle documentation and status updates
According to Deloitte, 45% of business tasks can be automated using RPA technology, with organizations achieving an ROI of 30-200% in the first year.
What Is Intelligent Automation?
Intelligent Automation Definition and Advanced Capabilities
Intelligent Automation (IA), also called Intelligent Process Automation (IPA), represents the convergence of RPA with cognitive technologies, primarily artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). IA combines RPA’s ability to automate well-defined tasks with AI capabilities that enable learning, decision-making, and adaptation.
Key IA Characteristics:
- AI and ML Powered: Uses machine learning algorithms that improve over time
- Unstructured Data Handling: Processes both structured and unstructured information
- Dynamic Decision Making: Makes context-aware decisions beyond simple rules
- Continuous Learning: Improves performance through experience and feedback
- Natural Language Processing: Understands and generates human language
- Computer Vision: Analyzes images and visual documents
- Complex Process Automation: Automates end-to-end workflows with multiple decision points
Advanced IA Capabilities Include:
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasts outcomes based on historical patterns
- Sentiment Analysis: Understands customer emotion and intent
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies unusual patterns or potential fraud
- Document Intelligence: Extracts meaning from unstructured documents (PDFs, emails, images)
- Intelligent Routing: Directs work based on complexity and skill requirements
- Automated Exception Handling: Self-corrects when encountering unexpected situations
IA enables automation of significantly more complex processes, with 72% of organizations strongly supporting intelligent automation strategies.
Core Differences: RPA vs Intelligent Automation at a Glance
Understanding the fundamental differences between RPA and IA helps determine which technology aligns with your business needs.
| Aspect | RPA | Intelligent Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligence | Rule-based, no AI capability | AI and ML powered with cognitive abilities |
| Data Handling | Structured data only (consistent format) | Structured and unstructured data |
| Decision Making | Predefined rules only (IF/THEN logic) | Dynamic, context-aware decisions |
| Learning | Static, no learning from experience | Continuous learning and improvement |
| Task Complexity | Simple, highly repetitive tasks | Complex workflows with multiple decision points |
| Implementation | Fast deployment (weeks to months) | Longer setup (months to quarters) |
| Initial Cost | Lower investment required | Higher upfront investment |
| Integration | UI-based, works with existing systems | APIs and multi-layer integration |
| Error Handling | Requires manual intervention | Self-correcting capabilities |
| Scalability | Moderate, limited by complexity | High, handles process variations |
| Adaptability | Requires manual updates for changes | Automatically adapts to variations |
The Market Opportunity: RPA and Intelligent Automation Growth
The automation market is experiencing explosive growth, with RPA leading and IA rapidly accelerating adoption.
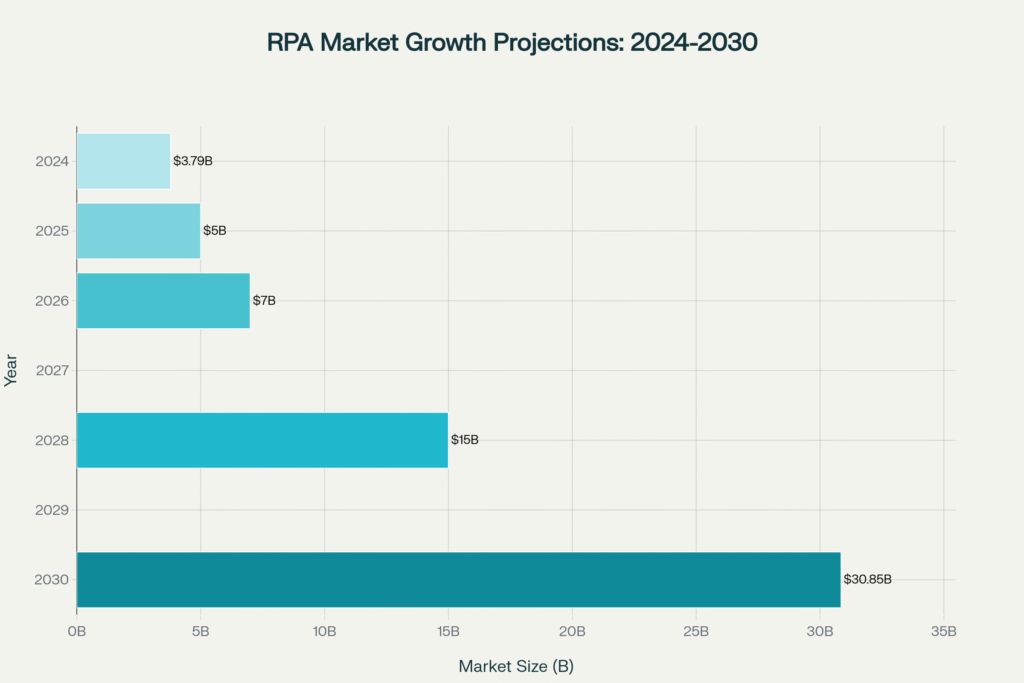
Projected growth of the global RPA market from $3.79 billion in 2024 to $30.85 billion by 2030, demonstrating the explosive 43.9% compound annual growth rate
RPA Market Expansion (2024-2030)
The RPA market demonstrates remarkable growth potential:
Market Size Evolution:
- 2024: $3.79-22.79 billion (source variance reflects different research methodologies)
- 2025: $5-7.01 billion
- 2030: $30.85-64.47 billion
- Compound Annual Growth Rate: 43.9%
Expected ROI from RPA:
- First-year returns: 30-200%
- Long-term potential: Up to 300%
- Financial services savings: $100,000 annually (52% of organizations)
Adoption Metrics:
- 53% of companies have implemented RPA
- 78% have implemented or plan to implement
- 98% of IT leaders believe automation is essential for financial gains
- 45-50% of business tasks are automatable
Hyperautomation Market Emergence
The convergence of RPA with AI creates hyperautomation, a market expected to reach $600 billion by 2025. Hyperautomation represents end-to-end process automation combining multiple technologies for maximum efficiency.
Hyperautomation Components:
- RPA for task automation
- AI and ML for intelligent decision-making
- Process mining for process discovery and optimization
- Advanced analytics for insights
- Workflow automation across systems
By 2025, Gartner predicts hyperautomation will impact one-fifth of all business processes, with organizations achieving greater agility and operational transformation.
When to Choose RPA: The Right Use Cases
RPA excels in specific scenarios where tasks are highly structured, repetitive, and rule-based. Understanding when RPA is the optimal choice helps ensure successful automation investments.
Ideal RPA Scenarios
High-Volume Repetitive Processes
- Invoice processing handles hundreds daily
- Data entry from standardized forms
- Report generation on fixed schedules
Structured Data Environments
- Data consistently formatted and located
- Clear input validation rules
- Minimal exceptions or variations
Well-Defined Business Rules
- Simple IF/THEN decision logic
- No judgment calls required
- Consistent workflow regardless of circumstance
Budget and Timeline Constraints
- Need quick implementation for immediate ROI
- Limited budget for complex solutions
- Want to prove the automation concept quickly
Legacy System Environments
- Cannot modify existing systems
- Need to work through user interfaces
- No API access available
RPA Industry-Specific Applications
Finance and Accounting
- Invoice processing and validation
- Expense report processing
- General ledger entries
- Financial close procedures
- Account reconciliation
Banking and Financial Services
- Know Your Customer (KYC) initial data collection
- Account opening documentation
- Transaction processing and settlement
- Loan application form completion
Insurance
- Policy issuance and document generation
- Claims form processing and routing
- Premium calculation from structured data
Human Resources
- Employee form filling during onboarding
- User account and system access creation
- HR system data entry
- Welcome notification distribution
Manufacturing
- Purchase order processing
- Shipment tracking updates
- Inventory system updates
Retail
- Order entry from structured sources
- Inventory updates
- Shipment tracking
RPA Benefits and Outcomes
- Organizations implementing RPA typically experience:
- Efficiency Gains: 30-70% process time reduction for automated tasks
- Accuracy: 99%+ accuracy compared to 80-85% human accuracy
- Cost Reduction: 30-70% labor cost savings for outsourceable tasks
- Speed: 24/7 operation without breaks or fatigue
- Compliance: Consistent process execution and full audit trails
- Employee Satisfaction: Staff freed from mundane work
Case Study: A financial services company automated invoice processing using RPA. They deployed 15 bots that processed 50,000 invoices monthly, reducing processing time from 8 hours to 30 minutes per day, saving 90 employee hours weekly and improving accuracy to 99.9%.
When to Choose Intelligent Automation: Advanced Requirements
Intelligent Automation addresses scenarios where processes involve complexity, unstructured data, and need for adaptive decision-making.
Ideal Intelligent Automation Scenarios
Unstructured Data Processing
- Scanned documents or PDFs requiring interpretation
- Customer emails with varied information
- Complex application documents
- Images or video requiring analysis
Complex Decision Making
- Multiple variables influencing decisions
- Context-dependent actions required
- Risk assessment needed
- Exception handling beyond simple rules
Continuous Process Improvement
- Need for ongoing optimization
- Processes that evolve over time
- Requirement for pattern recognition
- Fraud or anomaly detection
Customer-Facing Automation
- Need for personalized interactions
- Natural language understanding
- Sentiment and emotion analysis
- Dynamic response generation
Long-term Digital Transformation
- Building intelligent process capabilities
- Preparing for future complexity
- Competitive advantage through technology
- Operational model transformation
Intelligent Automation Industry-Specific Applications
Healthcare
- Drug discovery through pattern analysis across medical literature
- Clinical trial acceleration with intelligent patient matching
- Patient appointment scheduling with conversational AI
- Claims processing with complex eligibility determination
- Predictive patient risk stratification
Banking and Financial Services
- Anti-money laundering (AML) with behavioral pattern detection
- Loan application assessment with complex credit analysis
- Know Your Customer (KYC) with document intelligence
- Portfolio risk analysis with market prediction
- Fraud detection through anomaly identification
Insurance
- Underwriting with risk assessment algorithms
- Claims fraud detection using behavioral analysis
- Premium estimation with multiple factor analysis
- First Notice of Loss (FNOL) with intelligent guidance
- Claims triage based on complexity indicators
Retail
- Demand forecasting using AI prediction
- Personalized product recommendations
- Inventory optimization across locations
- Sentiment analysis from customer reviews
- Dynamic pricing based on demand patterns
Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance using IoT sensor data
- Quality control with computer vision
- Supplier evaluation through performance analytics
- Supply chain optimization with demand prediction
- Bill of materials creation from varied document formats
Legal
- Contract analysis and risk identification
- Clause extraction and standardization
- Legal document classification
- Compliance monitoring across documents
- Patent and trademark research
Intelligent Automation Benefits
Organizations implementing IA experience:
- Process Transformation: Automate 70-90% of end-to-end workflows
- Complexity Handling: Manage processes with multiple decision points
- Accuracy with Context: Decisions informed by comprehensive data analysis
- Adaptability: Processes improve automatically over time
- Scalability: Handle process variations at scale
- Customer Experience: Faster, more intelligent responses
Case Study: A healthcare organization implemented IA for claims processing involving multiple insurance types and coverage scenarios. The system achieved 94% automation of complex claims, reduced processing time from 7 days to 2 days, reduced errors by 68%, and improved customer satisfaction from 3.2 to 4.7 stars.
Decision Framework: Choosing Between RPA and IA
A structured evaluation helps determine the right automation path for your processes.
| Decision Factor | Choose RPA If | Choose Intelligent Automation If |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Primarily structured data | Mix of structured and unstructured |
| Process Complexity | Simple, well-defined workflows | Complex, multi-step processes |
| Volume and Frequency | High frequency, highly repetitive | Variable patterns and frequency |
| Decision Making | Simple IF/THEN rules | Context-aware, complex decisions |
| Learning Requirements | No learning needed | Continuous improvement required |
| Exception Handling | Manual intervention acceptable | Self-correcting required |
| Budget | Limited budget | Budget for innovation |
| Timeline | Need quick implementation | Can invest time for thorough setup |
| Long-term Vision | Short-term ROI focus | Digital transformation strategy |
| Industry Type | Finance, back-office operations | Healthcare, customer service, AI-critical |
The Automation Evolution: From RPA to Hyperautomation
The future of automation isn’t choosing between RPA and IA, but understanding how they evolve into comprehensive automation platforms.
| Stage | Capabilities | Timeline | ROI Timeline | Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Basic RPA | Rule-based task automation, UI interaction | Already deployed widely | 6-12 months | Mature |
| Stage 2: Intelligent Automation | ML and AI integration, Unstructured data handling | Current standard 2024-2025 | 12-18 months | Rapidly maturing |
| Stage 3: Hyperautomation | End-to-end process automation, Multi-tool integration | Expected mainstream 2025-2026 | 18-24 months | Growth phase |
| Stage 4: Generative AI | Content generation, Advanced analytics | Emerging now | 24-36 months | Early adoption |
| Stage 5: Agentic Automation | Self-governing AI agents, Autonomous decisions | Next 2-3 years | Long-term transformational | Innovation |
Hyperautomation Framework
Hyperautomation combines multiple technologies for comprehensive process automation:
The Hyperautomation Stack:
- RPA for task execution and workflow orchestration
- AI and ML for intelligent decision-making
- Process mining for process discovery and optimization
- Advanced analytics for insights and predictions
- Intelligent document processing for unstructured data
- APIs and integration platforms for connectivity
- Business process management (BPM) for orchestration
By implementing this comprehensive approach, organizations achieve 70-90% automation across their processes compared to 30-40% with RPA alone.
Implementation Strategy: Building Your Automation Journey
A phased approach from RPA to full hyperautomation maximizes ROI while managing risk.
Phase 1: Assessment and Strategy (Month 1)
Activities:
- Identify repetitive, rule-based processes for RPA
- Measure baseline metrics (cost, time, errors)
- Define clear ROI targets and success metrics
- Assess organizational readiness
Outcome: Prioritized list of automation opportunities with business case
Phase 2: RPA Foundation (Months 2-6)
Activities:
- Implement RPA for 3-5 high-volume processes
- Build internal RPA expertise and training
- Establish governance and monitoring frameworks
- Achieve quick wins demonstrating value
Expected Results:
- 30-50% labor cost reduction for automated processes
- 99%+ accuracy on structured tasks
- Quick ROI (6-12 months)
Metrics to Track:
- Process automation rate (percentage of steps automated)
- Cost per process unit (before/after comparison)
- Processing time reduction
- Error rates and accuracy
- Bot utilization rates
Phase 3: Intelligent Automation Enhancement (Months 7-12)
Activities:
- Identify complex processes for IA implementation
- Add AI and ML capabilities to existing RPA bots
- Enable unstructured data handling
- Improve decision-making automation
- Enhance employee productivity through automation
Expected Results:
- 50-70% automation of complex processes
- Improved decision accuracy through AI
- Better handling of exceptions
- Extended automation to new process areas
Phase 4: Hyperautomation Integration (Months 13-18)
Activities:
- Integrate multiple automation tools
- Create end-to-end workflow automation
- Enable intelligent process discovery
- Implement process mining capabilities
- Establish continuous improvement mechanisms
Expected Results:
- 70-90% end-to-end process automation
- Significant operational efficiency gains (25-35%)
- Competitive advantages through automation
- Foundation for generative AI integration
Phase 5: Optimization and Scale (Ongoing)
Activities:
- Monitor and continuously optimize
- Scale successful automation across organization
- Prepare infrastructure for generative AI
- Invest in advanced analytics and AI
- Update organizational processes and skills
Expected Results:
- Sustained automation benefits
- Scalable, repeatable automation processes
- Digital transformation enablement
- Readiness for next-generation automation technologies
Common Challenges and Solutions
RPA Implementation Challenges
Challenge 1: Bot Fragility and Maintenance
Issue: RPA bots break when interfaces or business processes change
Solution: Build flexibility into bot design, implement version control, establish governance for changes
Challenge 2: Scaling Difficulties
Issue: Individual bots don’t scale to enterprise level
Solution: Use centralized automation platform, implement process standardization
Challenge 3: Security and Compliance
Issue: Bots managing sensitive data require robust security
Solution: Implement encryption, access controls, audit logging, compliance monitoring
Challenge 4: Change Management
Issue: Employees resist automation affecting their roles
Solution: Focus on job enhancement not elimination, retrain staff, establish automation centers of excellence
Intelligent Automation Implementation Challenges
Challenge 1: Data Quality Requirements
Issue: AI models need sufficient training data
Solution: Invest in data governance, implement data cleansing, build data pipelines
Challenge 2: Model Accuracy and Bias
Issue: AI models must achieve required accuracy without discriminatory bias
Solution: Validate models extensively, monitor for bias, implement explainability
Challenge 3: Complexity of Integration
Issue: IA requires connecting multiple systems and platforms
Solution: Use integration platforms, APIs, start with simpler use cases first
Challenge 4: Skills Gap
Issue: Organizations lack AI and IA expertise
Solution: Build centers of excellence, partner with vendors, invest in training
Industry-Specific RPA and IA Applications
Understanding how RPA and IA apply across industries helps identify relevant use cases.
| Industry | RPA Use Cases | Intelligent Automation Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Finance & Accounting | Invoice processing, Data entry, Report generation | Fraud detection, Risk assessment, Budget forecasting |
| Banking | KYC documentation, Account opening, Transaction processing | Loan approval, AML screening, Portfolio analysis |
| Healthcare | Patient data management, Billing, Claims entry | Drug discovery, Clinical trials, Appointment scheduling |
| Insurance | Policy issuance, Claims documentation, Premium collection | Underwriting, Fraud detection, Premium estimation |
| Retail | Order processing, Inventory updates, Shipment tracking | Demand forecasting, Personalized recommendations |
| Manufacturing | Order processing, Inventory management, Shipment tracking | Predictive maintenance, Quality control, Supplier optimization |
| HR | Form filling, Account creation, Notifications | Document verification, Personalized onboarding |
| Customer Service | Ticket creation, Routing, Status updates | Sentiment analysis, Intelligent routing, Chatbots |
| Legal | Contract management, Document organizing | Contract analysis, Risk identification, Clause extraction |
| Supply Chain | Order processing, Inventory updates, Shipment tracking | Demand forecasting, Supplier evaluation, Route optimization |
Emerging Trends: Generative AI and Agentic Automation
The automation landscape is rapidly evolving with emerging technologies reshaping possibilities.
Generative AI Integration (2025-2026)
Generative AI is transforming automation capabilities by enabling:
Content Generation
- Automated report creation
- Email and communication drafting
- Document summarization
Advanced Analytics
- Pattern discovery in large datasets
- Predictive insights generation
- Anomaly detection at scale
Intelligent Decision Support
- Recommendations based on complex analysis
- Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
- Process optimization suggestions
Agentic Automation (2026+)
AI agents represent the next evolution, featuring:
Autonomous Operation
- Self-governing agents making decisions independently
- Minimal human oversight required
- Ability to handle unforeseen situations
Intelligent Adaptation
- Learning from outcomes and adjusting behavior
- Continuous process improvement
- Cross-process learning and knowledge sharing
Multi-Agent Collaboration
- Agents working together on complex processes
- Shared decision-making frameworks
- Emergent capabilities from agent interaction
These emerging technologies suggest 59% of C-suite executives are increasing automation and AI investments.
Selecting and Implementing RPA and IA Platforms
Leading platforms address different organizational needs and use cases.
Top RPA Platforms (2025)
- Blue Prism: Strong enterprise governance, scalable deployment
- Automation Anywhere: Robust AI integration, strong IQ Bot for document processing
- UiPath: Industry-leading features, extensive marketplace, developer-friendly
- SAP Intelligent RPA: Integration with the SAP ecosystem, enterprise focus
Leading IA and Hyperautomation Platforms
- Hyperscience: Advanced intelligent document processing and automation
- Datarails: AI-driven financial automation
- Brainware (Hyland): Document intelligence and capture
- Kopius: Enterprise hyperautomation platform
Selection Criteria
When evaluating platforms, assess:
- Business Requirements: Specific use cases you need to automate
- Scalability: Ability to handle growing volume and complexity
- Integration: Compatibility with existing systems
- AI Capabilities: Advanced features for planning the IA future
- Vendor Support: Training, implementation, and ongoing support
- Total Cost of Ownership: Licensing, implementation, and maintenance costs
Conclusion: The Path Forward in 2025 and Beyond
RPA and Intelligent Automation represent complementary technologies shaping the future of business operations. RPA excels at automating high-volume, repetitive, rule-based processes with quick ROI, while Intelligent Automation extends automation to complex, decision-heavy workflows requiring cognitive capabilities.
Key Takeaways
1. RPA Is Proven and Scaling
With 53% adoption and 43.9% projected growth through 2030, RPA is mainstream. Organizations implementing RPA achieve 30-200% first-year ROI and sustained cost savings of 30-70%.
2. Intelligent Automation Is Rapidly Emerging
72% of organizations support IA strategies, with 98% of IT leaders viewing automation as essential. IA enables automation of significantly more complex processes impossible for RPA alone.
3. Hyperautomation Is the Future
The $600 billion hyperautomation market by 2025 reflects the convergence of RPA, AI, process mining, and analytics. Organizations combining multiple automation technologies achieve 70-90% process automation compared to 30-40% with RPA alone.
4. Strategic Implementation Drives Success
Phased approaches starting with high-impact RPA projects, then gradually adding IA capabilities, maximize ROI while managing risk. Organizations should plan for evolution from RPA to hyperautomation over 18-24 months.
5. Generative AI Will Transform Automation
Emerging generative AI and agentic automation capabilities will fundamentally reshape what’s automatable. Organizations investing now will lead in next-generation automation competencies.
6. Skills and Change Management Matter
Technical selection is secondary to organizational readiness. Success requires investment in training, change management, and cultural transformation toward an automation mindset.
Your Next Steps
- Assess your processes: Identify which fall into the RPA sweet spot vs. requiring IA
- Define your strategy: Create a roadmap from the RPA foundation to the hyperautomation vision
- Start small: Launch pilot projects with high business impact and low risk
- Build expertise: Develop internal automation centers of excellence
- Plan for evolution: Ensure platform choices support progression to IA and hyperautomation
- Focus on ROI: Measure and communicate automation benefits to sustain executive support
The automation economy is here. Organizations that effectively combine RPA, Intelligent Automation, and emerging technologies like generative AI will lead in digital transformation, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
The question is not if your organization will automate, but how quickly and effectively you’ll embrace these transformative technologies. The companies that start their automation journey today will be positioned to scale intelligent automation at the enterprise level by 2026, gaining decisive competitive advantages in their industries.
Comments