Machine learning has become the engine powering modern AI—from self-driving cars and medical imaging to content moderation and voice assistants. But behind every impressive AI application lies a less glamorous, labor-intensive, and absolutely essential foundation: AI data labeling.
While cloud giants like Google and Amazon define data labeling in straightforward terms—adding meaningful tags to raw data—the reality inside enterprises is far more complex. Today, data labeling is not merely a preprocessing task; it is a competitive differentiator that determines the performance, accuracy, and fairness of machine learning systems.
In 2025, the organizations that excel at data labeling—both in quality and scale—are the ones building AI models that outperform the competition.
This deep-dive blog explains what AI data labeling really is, why it matters, how it works, and how modern teams can build gold-standard datasets that fuel reliable ML systems.
What Is Data Labeling?
Data labeling is the process of adding structured information—known as annotations—to raw data so that machine learning models can understand, learn from, and make decisions based on it.
When a human annotator labels an image as “dog,” an audio clip as “applause,” or a text sentence as “negative sentiment,” that label becomes a teaching signal for the model.
Think of labeled data as the ground truth curriculum for AI:
➡ The better the curriculum, the smarter the model.
Without labeled data, a supervised machine learning model has no context, no understanding, and no direction.
Why AI Data Labeling Matters More Than Ever
Google and Amazon both emphasize that labeled data is required for supervised learning—accurate labels equal accurate models. But the real story is deeper.
1. Labeled Data = Model Accuracy
Even the most advanced neural network is only as good as the data it learns from. Poorly labeled datasets lead directly to:
- Lower prediction accuracy
- Biased output
- Unstable model behavior
2. Labeled Data Mitigates AI Bias
Models trained on unbalanced or incorrectly labeled datasets inherit those mistakes—at scale. Proper labeling enforces:
- Balanced representation
- Fairness
- Clear edge-case handling
3. Labeled Data Accelerates Automation
Automation can only happen reliably if the model understands the world with clarity. High-quality dataset labels power:
- Automated tagging
- Search relevance
- Content recognition
- Conversational AI
- Vision systems
4. Labeled Data Enables High-Performance AI (CV, NLP, Speech)
Everything from ChatGPT to Tesla’s Autopilot relies on millions of carefully labeled examples. There is no shortcut.
Data labeling is not just a task—it is the foundation of modern AI.
How Data Labeling Actually Works
While cloud providers describe labeling as assigning tags to data, real-world data labeling workflows involve coordination across tools, people, processes, and quality pipelines.
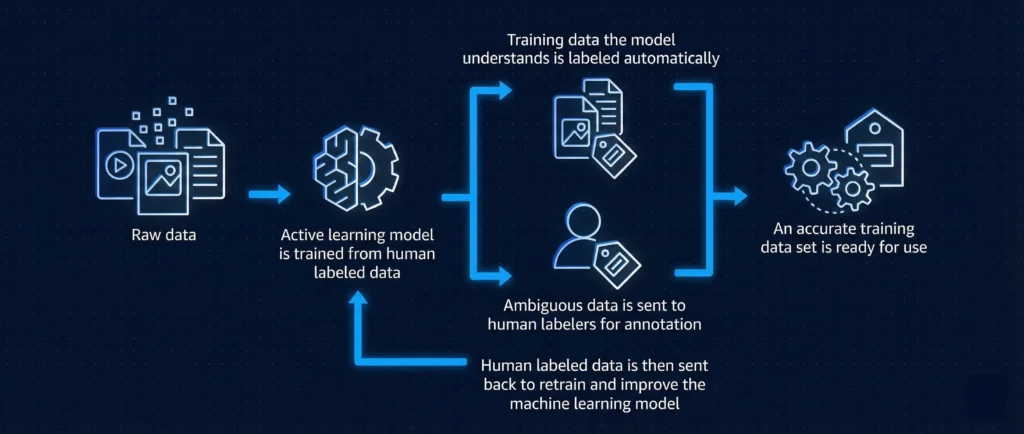
Here’s a deeper look at how professional data labeling operations function.
1. Defining Labeling Guidelines
Good labeling begins with clear instructions—arguably the hardest part of the entire pipeline. Teams must define:
- Label taxonomies
- Annotation boundaries
- Edge cases
- Hierarchies
- Ambiguous scenarios
A single unclear guideline can corrupt thousands of data points.
2. Selecting Labeling Tools
Depending on the data type, organizations select:
- Image/video annotation platforms
- Text labeling UIs
- Speech transcription systems
- Sensor/time-series labeling dashboards
Tools such as Scale AI, Labelbox, SuperAnnotate, and Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth support enterprise workflows.
3. Training Annotators
Human annotators—internal teams or outsourced workers—must fully understand:
- Label definitions
- Examples and counterexamples
- Annotation boundaries
- Mistake patterns
Training consistency is crucial because inter-annotator reliability determines dataset quality.
4. Performing the Labeling
Annotators manually assign labels, correct automated suggestions, or verify machine-generated predictions. This is the core labor of data labeling.
5. Quality Control (QC)
The most sophisticated AI companies use multi-layered QC systems:
- Consensus scoring (multiple annotators)
- Reviewer audits
- Automated flagging for low-confidence labels
- Statistical sampling
A dataset is only as reliable as its QC pipeline.
6. Integrating Labels Into ML Pipelines
Once validated, the labeled dataset becomes the training, validation, and testing corpus for machine learning models.
Types of Data Labeling (With Real AI Use Cases)
While Google and Amazon list categories, let’s expand them with modern AI examples.
Image Labeling
Used for:
- Self-driving cars
- Medical image diagnostics
- Product recognition
- Quality inspection in factories
Types include bounding boxes, polygons, keypoints, segmentation masks.
Text Labeling
Used for:
- Chatbots
- Search relevance
- Sentiment analysis
- Document summarization
- NER (Named Entity Recognition)
Tasks include tagging emotions, intent, grammar roles, or entities.
Audio Labeling
Used for:
- Automatic speech recognition (ASR)
- Emotion detection
- Smart home devices
- Wildlife sound monitoring
Tasks include transcription, speaker ID, acoustic event tagging.
Video Labeling
Used for:
- Autonomous driving
- Sports analytics
- Security systems
- Human activity recognition
Requires frame-by-frame tracking and complex temporal annotation.
Time-Series Labeling
Used for:
- Predictive maintenance
- Financial anomaly detection
- IoT sensor analysis
Labels identify spikes, failures, or specific event patterns.
Audio Labeling
Used for:
- Automatic speech recognition (ASR)
- Emotion detection
- Smart home devices
- Wildlife sound monitoring
Tasks include transcription, speaker ID, acoustic event tagging.
Video Labeling
Used for:
- Autonomous driving
- Sports analytics
- Security systems
- Human activity recognition
Requires frame-by-frame tracking and complex temporal annotation.
Time-Series Labeling
Used for:
- Predictive maintenance
- Financial anomaly detection
- IoT sensor analysis
Labels identify spikes, failures, or specific event patterns.
Manual, Automated, and Hybrid Data Labeling: Which Works Best?
Here’s a clearer comparison than Google or Amazon provides:
Comparison Table
| Method | How It Works | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Labeling | Humans annotate data directly | Highest accuracy, nuanced understanding | Slow, expensive | Medical AI, self-driving, critical datasets |
| Automated Labeling | ML models pre-label data | Fast, scalable | Can propagate model errors | Large low-risk datasets |
| Hybrid Labeling | Human-in-the-loop correcting machine labels | Best balance of quality & efficiency | Requires tooling + workflow sophistication | Enterprise AI teams, complex ML pipelines |
Nearly all successful AI teams today use hybrid labeling, where humans refine machine suggestions. It maximizes efficiency while protecting dataset integrity.
How AI Data Labeling Is Becoming More Efficient
Amazon highlights active learning and label auditing—but the modern landscape is even broader.
AI-Assisted Labeling Is Now the Norm
Models pre-label data with confidence scores. Humans only review:
- Low-confidence predictions
- Edge cases
- Uncertain boundary regions
This reduces manual work by up to 70% in some enterprises.
Synthetic Data Is Emerging
AI-generated data fills gaps where real-world labels are scarce—such as rare defects or hazardous driving scenarios.
Programmatic Labeling
Tools like Snorkel let teams write labeling functions—rules that automatically annotate data.
Foundation Models Speed Up Annotation
General-purpose models now help with:
- Summarization
- Entity extraction
- Scene description
- Audio transcription
Instead of replacing human annotators, they amplify them.
How to Build a High-Quality AI Data Labeling Pipeline
If you want a dataset that outperforms competitors, invest in:
Platform choice directly influences throughput, quality, and scalability, which is why reviewing the top data labeling & dataset platforms can help teams select systems aligned with their ML roadmap.
1. Clear, unambiguous labeling guidelines
Include examples, counterexamples, and standardized decision rules.
2. Diverse and representative data
Avoid skewed datasets that create biased or brittle models.
3. Multi-layer quality control
Consensus scoring, audits, inter-annotator agreement, and algorithmic QC.
4. Privacy-first data handling
Encrypt data, restrict access, and anonymize sensitive elements.
5. Continuous iteration
If models misbehave, revisit the dataset—not just the architecture.
6. The right tools and hybrid labeling workflow
Data labeling is not scalable without a strong platform foundation.
Conclusion: Data Labeling Is the Unsung Hero of AI Performance
AI breakthroughs are often attributed to model architectures, GPUs, or clever algorithms. But none of these matter if your labeled data is flawed.
Google and Amazon define data labeling correctly—but the real world of AI shows that labeling is strategic, iterative, and mission-critical.
AI data labeling is the quiet work that determines:
- How well your model performs
- How fairly it behaves
- How safely it operates
- How much it costs to maintain
- How reliable it is in production
In many ways, great AI isn’t built—it’s labeled.
Comments
You made an excellent point about how crucial accurate data labeling is for the success of AI models. It’s fascinating how even small errors in labeling can lead to significant mispredictions, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare or autonomous driving.